What is Regenerative Finance (ReFi)?
Regenerative Finance (often shortened to ReFi) is a transparent, accessible, and inclusive alternative to traditional financial systems. We'll explore the basics of ReFi, and look into what it can mean for individuals and businesses.

A quick summary📜
Regenerative Finance — often shortened to "ReFi" — is an inclusive, transparent, and accessible alternative to conventional financial systems. ReFi opens avenues to embed care for communities, living ecosystems, and our environment into the roots of our economic system. In a regenerative financial system, economic activity benefits all of the system's living participants, instead of unsustainably extracting resources, unfairly distributing profits, and ignoring the value of living ecosystems. Although still in its early stages, ReFi has the potential to fundamentally transform how we use money and finance as tools to help life thrive on our planet.
Why we’re writing this piece
You might have heard the term ReFi (or Regenerative Finance), or seen it mentioned. And you've probably wondered: what actually is ReFi? Is this a real system that already exists, an idea, or an economic theory? Currently, it's a bit of each: ReFi is a new idea that's starting to get attention, and there are existing ReFi projects that are making a real difference for people and ecosystems around the world. Although ReFi is still in its earliest stages — the term was first mentioned in 2019 — certain patterns have started to emerge.
The environmentalist Paul Hawken describes it as follows: "Regeneration means putting life at the center of every action and decision."
On a more practical level, regeneration is the ongoing process of replacing or restoring damaged or missing elements in complex systems so they maintain full functionality in the near and far future.
To us at Toucan, regeneration is also a measure of the breadth and depth of life. Regeneration enables living beings to fulfill their potential and express their ability to live. Being regenerative also means being mindful of the impact of our actions, as they influence how well life on Earth can flourish, now and in the future.
People often associate ReFi with being limited to greenhouse gas emissions or carbon credits, but the underlying ideas and potential are much bigger. It's crucial to educate everyone about what ReFi is now, what it can become, and which opportunities can arise through a regenerative financial system. If people understand how ReFi works, they are better equipped to participate and help shape this new system. ReFi also is an exciting space where climate-conscious people with a financial or tech background can put their talent to work on something impact-driven. This fits perfectly into today’s focus on doing work that isn’t just financially rewarding, but also meaningful on a higher level.
In this article, we'll explore the basics of ReFi and look into what it can mean for individuals and businesses.
Read on or jump to the sections you're most interested in 👇
- Building on the shoulders of giants: Regenerative Economics thinkers
- Comparing conventional & regenerative economic systems
- Why is ReFi emerging now?
- Web3 is paving the way for Regenerative Finance
- DeFi — a financial system emerging from the Web3 movement
- ReFi as an evolution of DeFi
- How can we trust that ReFi is real and not a scam?
- ReFi as the first big real-life use case of Web3
- Diversity in ReFi
- Exploring different areas of ReFi
- How does Toucan implement ReFi?
- Our favorite ReFi resources
Building on the shoulders of giants: A short stroll through history
The idea of a regenerative economy is not new. For a long time, economists have been thinking about how to systematically embed care for our planet and for communities into the way our world works, and studying how financial policies affect social and ecological well-being. Regenerative economic theories look into improving the well-being and health of communities and nature by addressing issues like poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation.
Some ideas of regenerative economics include, encouraging conscious spending and consumption, promoting the efficient use of resources, and prioritizing well-being over growth.
For decades, thinkers, economists, and philosophers have been suggesting alternative visions of a more just and sustainable economy. Let's recap some of their ideas:
- In 1916, economist Silvio Gesell proposed "Freigeld," a spending-power stable currency with a negative interest rate, to incentivize circulation and discourage the hoarding of money. This property, called "demurrage", would boost economic activity and improve the lives of people, particularly those in poverty.
- In the late 1800s, Henry George advocated for a land value tax to address wealth inequality and promote economic growth, by taxing something that cannot be created or destroyed.
- Elinor Ostrom's work challenged the conventional wisdom that common-pool resources are doomed to fail unless they are privatized or regulated by the state. She showed that communities can manage these resources sustainably and equitably through cooperation, communication, and trust. Ostrom won the Nobel Prize for economics in 2009.
- Kate Raworth's doughnut model identifies a "safe and just space for humanity" by setting a lower limit for basic human needs and an upper limit for planetary boundaries.
- Charles Eisenstein's “Sacred Economics” thesis proposes that money is not just a medium of exchange or store of value, but also a symbol of a society's values and beliefs. He argues that the way in which money is designed reflects a society's moral and ethical systems.
- John Fullerton's thinking asserts that money is not just a practical tool, but also a reflection of the spiritual and cultural values of a society.
Now, advancements in computing including blockchains and smart contracts mean we have the technology that allows us to realize the visions of these thinkers, and to expand on their work.
ReFi is regenerative finance; an economic system that grows in capacity over time and is resistant to shocks. Regenerative finance can mean regeneration of financial systems, but it can also mean the regeneration of social, material, living, intellectual, experiential, spiritual, and cultural capital as well. ReFi is the key to human flourishing in the 21st century.
Kevin Owocki, Gitcoin Co-Founder
By building on the theoretical foundation laid by previous generations, innovators in ReFi are working to create a regenerative economic system that prioritizes the well-being of all life and the planet.
Conventional & regenerative economic systems
A comparison
Here's a quick comparison of conventional and regenerative economic systems:
| Conventional system | Regenerative system |
|---|---|
| Value is used to extract more value |
A portion of the value flows back to communities & planet |
| Exponential growth | Healthy growth & sustainable maturation |
| Systems serve capital | Systems serve people & the planet |
| Growth at the expense of planet & community |
Growth promotes the health of planet & community |
| The more active the system, the more resources are being consumed |
The more active the system, the more regeneration happens |
| Economic and financial health is separated from other indicators of prosperity |
Economic and financial health are inseparable from human, societal, and environmental health |
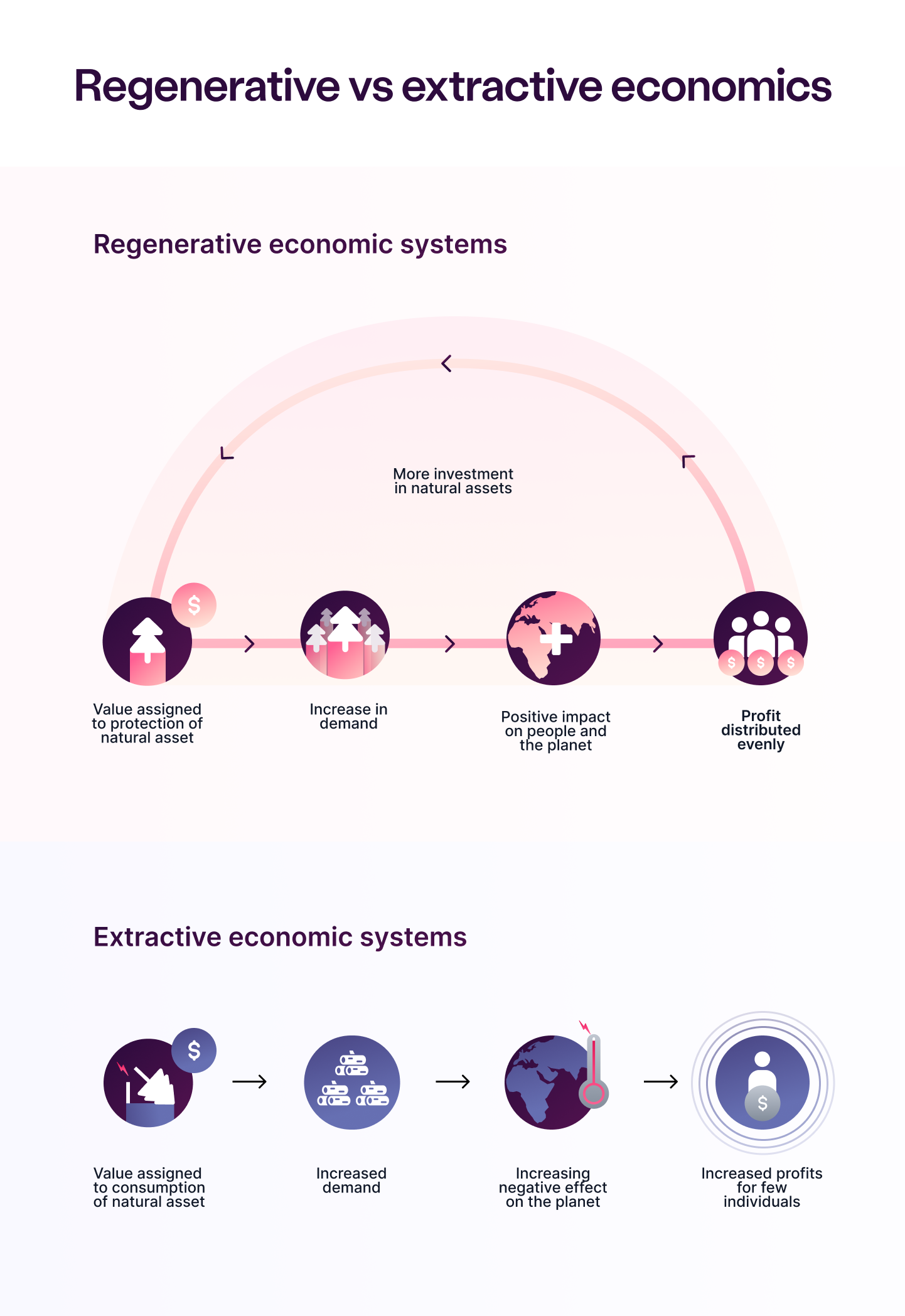
A regenerative economic system actively works towards restoring and replenishing natural resources and ecosystems, instead of exploiting them for short-term gains. It prioritizes creating sustainable and equitable prosperity for all, while preserving the planet's natural resources. Businesses and individuals are motivated and incentivized to act in the long-term interest of the planet and its inhabitants, rather than solely being focused on maximizing profit for themselves.
Regenerative economic systems can include
- regenerative agriculture
- circular economy models
- renewable energy
- policies that promote social and economic justice
and several other models, which we'll explore here.
Why is ReFi emerging now?
The Regenerative Finance movement is emerging as one potential way to address many problems of our time. The climate crisis is posing one of the biggest threats that humanity has ever faced. People are becoming more and more aware of issues of inequality, exploitation, and unsustainable industrial practices. Over the last few decades, the limits of many elements of the world's economic models have become apparent. Our economic system lacks the right incentives, and there’s no way to coordinate at the level needed in a globalized world. We have plenty of resources available to address inequalities, but they often end up in the wrong hands or they can’t be distributed to the right places due to simple friction points, like issues with transferring money. Additionally, a lack of transparency in our systems has made it easier for unprincipled actors to extract profits.
ReFi offers the theoretical framework, but also advanced tools, like blockchain technology, to tackle these issues head-on. Based on open code and secure ledgers stored on consensus networks, ReFi offers a way to implement a more democratic and inclusive alternative to traditional financial systems. ReFi rails can be programmed to fairly reward key actors and redirect resources to those who need them most while holding all participants publicly accountable. The entire system prioritizes fairly distributed, sustainable, and equitable prosperity.
Web3: paving the way for Regenerative Finance
Web3 is a movement that has emerged over the last years, and it is far more than the evolution of the internet. We classify Web3 as a set of design principles that are adopted by a strong community of individuals around the globe. Web3 aims to build user-centric digital spaces and services that are accessible to everyone, regardless of their background, nationality, or other factors. Blockchain technology is one of the key tools that makes the Web3 transition possible.
Web3 is often called the next iteration of the internet. This refers to the internet's basic functionality: Web1 was mainly a source of information where people could read content. In Web2, they were able to read, but also create their own content. And in Web3, everyone can read, create, and also own the content they’ve put up. While this is accurate, there's way more to Web3!

- Transparent: Financial activity is publicly recorded in a tamper-proof database. Each participant can verify that the activity of others meets mutually-agreed rules.
- Decentralized: There is no single company or individual actor who can unilaterally set rules or define how users should behave without their consent.
- User-controlled: Each participant can access their data and assets independent of anyone else.
- Censorship-resistant: At the base level, no one can dictate what content is acceptable and what content isn’t, because there are no central parties controlling access.
- Accessible to everyone: No gatekeepers exist, and no permission or approval is necessary to access Web3 systems. There are no limitations in functionality based on country or status.
- Interoperable: Everyone can build on top of or with existing systems without needing anyone else's approval.
Blockchains directly connect users and developers around the world with each other, allowing them to exchange goods, services, information, and digital assets. With the help of blockchain technology, we can lay the foundation for systems that are open, fair, and democratized.
Web3 systems are designed to be open to everyone, but that doesn't mean it's impossible to apply safety controls like know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) checks. These security measures can consciously be added to certain parts of an application or service to protect users, while still adhering to the underlying idea that by default, people have a right to access them as public goods.

Web3 applications span a wide range of areas, from democratic digital governance systems to decentralized applications (dApps) for financial and other services. There are digital public goods, such as currency exchanges that aren’t owned or controlled by a company, and even a variety of metaverses and digital games where you can seamlessly move your assets from one virtual world to the other.
As Web3 continues to evolve, we expect to see more innovative and impactful projects emerge, to bring the benefits of blockchain technology to the real world.
Blockchains & smart contracts explained
Blockchains offer a secure and public way to store and share information across a network of computers. Once information is added to the blockchain, it can't be altered or deleted by anyone — that’s why people often say that blockchains are a “tamper-proof storage of data”.
Smart contracts are essentially small computer programs that are stored and run on the blockchain, and they can interact with information that has been saved on-chain. Smart contracts can execute a variety of actions based on predefined conditions. A smart contract could, for example, automatically buy and retire tokenized carbon credits whenever a user sends funds from one account to the other.
Anyone can add new smart contracts to an open blockchain like Ethereum, and these new smart contracts can freely interact with everything that’s already there. This is because smart contracts are “interoperable”, or "composable". Developers can create applications and services that expand on existing ones, which unlocks unbridled innovation, and ultimately benefits the entire ecosystem.
What is DeFi?
A financial system emerging from the Web3 movement
DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is a new, accessible, and inclusive financial system that has emerged out of the Web3 movement. It directly connects people with financial services and replaces middlemen with decentralized software applications built with smart contracts.
Built with open code on decentralized public blockchains, DeFi offers a more democratic, transparent and, in many ways, secure alternative to traditional finance. As DeFi continues to evolve, this system has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about and interact with money.
Quick comparison — DeFi and TradFi (or "finance as we know it")
| DeFi | TradFi | |
|---|---|---|
| Sending money | Directly to peers | Via middlemen (i.e. banks or digital payments platforms) |
| Interest rates | Programmed into smart contracts, set by a transparent governance process | Set by small centralized groups, often in private |
| Using individual services | One or a few accounts for all services | Option to use many accounts |
In DeFi, services often offered by companies or other centralized parties (i.e. banks or stock exchanges) are replaced by smart contract applications. These computer programs can run and maintain different financial products such as single and joint bank accounts, lending services, or currency exchanges.
Open-source code or software is released under a license that grants users the right to use, study, or change this software and its code – no matter the purpose. Open code refers to a codebase that is available for everyone to read (for example on Github), but that doesn't necessarily mean it's also open source.
Theoretically, everyone can audit every single one of these services whenever they want, without the need to ask anyone for permission or for the data. Even consumers that don’t know how to read smart contracts or analyze blockchain data benefit from the auditing capacity of a broad range of individual reviewers, instead of having to trust one organization to perform audits behind closed doors. This previously unknown level of transparency is one of the main value propositions of Decentralized Finance. What other benefits does DeFi have?

Value extraction is minimized. No intermediaries or middlemen are setting their own (often obscured) rates. Any transaction fees taken to sustain the service are transparent to everyone.
Even actors with little capital can participate in DeFi, and they enjoy the same conditions (i.e. interest or exchange rates) as those with ample economic resources. This equitable access sharply contrasts with guard-railed systems in traditional finance.
Individuals also have full control over their funds at all times, even though these funds don’t sit in the form of physical coins or notes in anyone's wallet or safe. In comparison: In conventional banking systems, deposited money is custodied and often re-invested by banks or other parties. It’s not always clear where your bank invested your funds, and what risk profile they have chosen.
DeFi is especially relevant for those who have little or no access to banking services. It helps further financial inclusion for everyone, as entry barriers are reduced.
Two examples of DeFi products
Decentralized lending platforms can be compared to bank accounts with a peer-to-peer lending function. They allow users to earn interest on their crypto holdings, or borrow crypto assets from others. Traditional banks often have strict lending criteria and may charge high fees. In contrast, DeFi lending platforms are accessible to everyone (as long as the lender is able to provide collateral), and they often offer very competitive interest rates.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXes) let users trade cryptocurrencies without the need for intermediaries. Instead of matching buy and sell orders, often DEXes enable exchanges with "liquidity pools". Users deposit funds into a pool (these users are called Liquidity Providers or LPs), and everyone can freely trade their funds with what's in the pool. Exchange rates are calculated based on supply and demand by the DEX smart contracts, and conditions like trading fees are set transparently. Only transactions that match predefined criteria are approved — for example, which funds can be exchanged against each other. DEXes are accessible to anyone with an internet connection and a crypto wallet; there’s no need to go through lengthy verification processes to open an account. Exchanging funds via a DEX is fast, and transaction fees are marginal.
Of course, there is risk involved. Applications on a blockchain could be poorly designed or malicious — after all, access is open so anyone can create a decentralized application. Not many regulations are in place yet, so users of DeFi products need to carefully evaluate which services are safe to use and trustworthy.
We recommend that you thoroughly familiarize yourself with the world of DeFi before participating in it and that you don’t deposit more funds than you could afford to lose. A broad range of safety checks have emerged as best practices, and large DeFi protocols have been securely offering users around the world financial services for several years now.
ReFi – the evolution of DeFi
The exchange of value within communities and economies is fundamental to how our world operates. Digital tools like blockchains are giving us advanced ways to design and reprogram value exchange mechanisms and money flows, and let us include what we value in our financial systems.
ReFi — or Regenerative Finance — has evolved out of DeFi. It builds on the principles of its predecessor, and interweaves them with theories and approaches from regenerative economics. ReFi expands on some DeFi principles and replaces others to realize the idea of a regenerative and inclusive economic system. Many traits of ReFi are derived from DeFi, for example, that people have control over their funds, and that applications, services, and transactions are transparent and openly accessible.

Early uses of ReFi include designing novel ways to fund public goods (like open source software) and tokenizing environmental assets (like carbon credits) so they could be used in DeFi applications (like DEXes). Now, ReFi is rapidly expanding in other directions as well.
While ReFi relies on digital tools and the Internet, it is already creating positive physical and tangible outcomes for people worldwide. Everyone can leverage ReFi's digital infrastructure to coordinate and pool resources across borders, design products that serve key needs for local communities, or build services that accelerate climate action.
What's important to remember: ReFi isn't just a new way to access financial services. ReFi seeks to build a financial system that generates positive environmental and social outcomes — an economy that is regenerative by design.
What are the key traits of ReFi systems?

Globally accessible: People from all over the world can participate in Regenerative Finance systems. This makes ReFi a powerful tool for promoting financial inclusion, overcoming censorship, and coordinating across borders.
Automating positive actions: ReFi systems enable the advanced coding of desired behaviors directly into the core of economic systems. In reality, this means that a ReFi application could automatically compensate for its own emissions, or send a portion of the exchanged value to communities in need of funding. Economic growth can now be aligned with environmental or humanitarian goals.
Very flexible: ReFi tools are rapidly adaptable, and they can be quickly and easily modified to maximize their impact whenever it’s necessary. They can be adjusted in response to changing market conditions, and to address new scientific evidence and other emerging opportunities.
Eliminating friction points: ReFi eliminates many friction points of traditional financial systems. For example, it can easily and cheaply facilitate the transfer of resources from the Global North to the Global South, making it easier for people in developing countries to access the financial services and capital needed to develop and flourish.
Fast and efficient: The exchange of money in ReFi systems is faster and more fluid than in traditional finance systems. Again, this allows for a more efficient and effective allocation of resources, including capital along with ideas or products.
Not under a single jurisdiction: ReFi systems are built by organizations operating in a range of regulatory jurisdictions, meaning they are resilient to risks posed by any single nation-state unexpectedly changing policies or collapsing.
Is the ReFi movement real?
Or could this be a scam?
Financial tools with open access, open code and open data unlock unbridled innovation, but openness can also allow bad actors to join that are trying to abuse the system. For users of these new systems, it's key to be cautious and aware and to do your due diligence before using a ReFi (or any Web3) service. Be thorough when evaluating new projects, and don’t put money into anything you don’t understand.
Many ReFi projects, like Toucan, are taking additional steps to keep users safe, and they are ensuring that processes are executed in a fully compliant way, for example by collaborating closely with relevant financial authorities or industry bodies.
ReFi systems can also pursue other avenues to minimize the risk of fraud. These include:
- making fully transparent codebases available for anyone to view
- offering public auditability, which allows anyone to review the code and transactions on the blockchain
- technical audits (i.e. code reviews) by top blockchain security firms
- bug bounties to reward anyone who identifies vulnerabilities.
Additionally, ReFi projects often have a strong community of users and developers who are invested in the success of the project. They often help identify and address any issues they spot.
While it's important to be aware of the risks associated with any new technology, ReFi has the potential to offer a more democratic, inclusive, and sustainable approach to how money works. By leveraging the advanced technologies we have at our disposal, ReFi applications can provide the transparency, security, and efficiency that traditional finance systems often lack, and make sure that caring for life on Earth is a core purpose of our economy.
ReFi: The first big real-life use case of Web3
Unlike many other Web3 applications, ReFi is strongly connected to the real world, and it often directly touches peoples' lives, along with real-world assets like carbon credits. That’s great, as it brings the actual utility of blockchain technology into focus, instead of zooming in on technological advancements, or enforcing a (too) radical change to old systems and approaches.
In ReFi systems, financial value can flow out of the cryptocurrency space and into a small-scale carbon farmer's bank account. In comparison: In DeFi, much of the circulating money never leaves the space, and isn’t converted into Euros or Dollars.
Because ReFi is so strongly focused on regenerating the planet and helping people, its community welcomes a more pragmatic and flexible approach to some Web3 principles and allows for trade-offs, if necessary. ReFi users also often value safety over experimental services with potentially high returns, and prefer knowing who they’re dealing with over prizing anonymity. For example, ReFi projects may implement KYC measures and screen users, instead of being completely permissive and open. Precisely these safeguards and identity checks make actors outside of Web3 more comfortable with using ReFi applications and services, which in turn helps speed up mass adoption, and makes ReFi more accessible and inclusive.
ReFi is the consciously programmed flow of value through specific incentives to people doing relevant work.
Andy Tudhope, Kernel
ReFi projects also may be more centralized to help steer novel systems in the right direction, and their founders might be in close collaboration with actors outside of the Web3 world, such as policymakers, non-profit leaders and corporate executives.
Example: Toucan's Carbon Bridge
Toucan's Carbon Bridge connects conventional carbon credit registries with an open, blockchain-based meta-registry, the Open Climate Registry. This Carbon Bridge will likely never be fully permissionless. There needs to be a way to verify that only certified carbon credits are being moved on-chain, where they can then be traded or integrated into other blockchain-based applications.
Two examples on how ReFi can touch people's lives
Carbon markets: A carbon credit represents a ton of carbon dioxide that has been removed or never been emitted into the atmosphere due to the work of an impact project. Once tokenized, this carbon credit can be sold directly by the project developer to a corporation or individual, without any intermediaries taking fees. The buyer could then deposit their carbon token into a decentralized lending service and earn a return. Additionally, the project developer could program royalties into his carbon tokens – whenever they are traded, he will receive a percentage of the sales price. This creates a win-win situation where investors benefit, while climate-positive initiatives are directly supported.
Climate investments: ReFi project EthicHub uses a specifically designed currency to enable frictionless cross-border money transfers from investors to borrowers such as regenerative farmers. This gives regenerative farmers easier access to capital to improve or scale their farming practices, while investors profit from higher interest rates than elsewhere. At the same time, the investor transparently supports those contributing to climate action.

As ReFi continues to evolve, we can expect to see more and more innovative and impactful projects emerge and bring the benefits of blockchain technology to the real world.
How diverse is the ReFi space?
Historically, the crypto industry hasn’t been very diverse. It was mostly dominated by white men, on the investor- as well as on the founder side. Between 2012 and 2018, only 18% of founding teams had a woman on board, and just 8% of founding teams were women-only.
But why is that? Women and people from developing countries often hesitated or were not able to access education that provides the technical skillset to participate in this new industry. They might also be more hesitant to take big career risks, or prefer to focus on working for established tech companies rather than experimental startups.
But, on the flip side, blockchain technology makes it easier than ever to launch diverse remote-only teams with members from all parts of the globe, or to contribute to decentralized organizations. Opportunities in Web3 and ReFi are often removed from the barriers traditionally presented by the world — from geographical boundaries to economies of scale. Decentralization, by design, also accelerates diversity and enables anyone interested to participate in the system, regardless of who they are and where they are from. This creates jobs for a very diverse workforce of passionate people. Many of them just need the right entry point to get involved.
ReFi provides such an entry point: People might hesitate to participate in the DeFi or NFT space, as the first is very financialized, and the second can feel like it’s just a big bubble. But they recognize the unique value proposition and tangible impact of a regenerative financial system. ReFi shows that the crypto space is much more than just technology and finance; it has the potential to promote the things we all value, like financial inclusion, democracy, and ecological sustainability.
This leads to minorities and marginalized groups turning to ReFi, and using it as a tool for innovation and growth, often at a faster pace than people from communities with more privileged access to resources. In ReFi, there are no gatekeepers telling minority developers, founders, or creators what to do; everyone can just build or contribute to whatever they see lacking or what’s serving the needs of communities and environments.

Lastly: There is a strong consensus among founders and users of the ReFi space on how important it is to aid diversity, as we can only construct a system that serves all stakeholders if we have them all in the same room!
Exploring different areas of ReFi
The ReFi space is rapidly evolving, but it’s still in its infancy and only now taking shape. At this stage, it's hard to define exactly what projects and initiatives are “truly ReFi” and which ones aren't. Many people and organizations are trying to tackle the task of mapping out the borders of the ReFi movement.

Let’s look at where else we see ReFi initiatives shaping up:
UBI
Universal basic income, or UBI, is a system where everyone is given a set amount of money on a regular basis. It's conditionless and available to anyone, regardless of their background, education, nationality, or income. UBI can function as a safety net for people, and it is supposed to ensure that everyone has a basic standard of living and can cover basic needs. Projects like Proof of Humanity, Circles and GoodDollar offer an unconditional UBI payment to all members trusted by other members of their respective communities. Digital technologies, and especially Web3 tools, show a lot of promise to help provide UBI to people around the world.
Local currencies
Communities can create local currencies to ensure that economic activity can flow within their local community, and to promote values they care about. With carefully designed rules, funds are circulating to regenerate and fuel the local economy, and to help satisfy the needs of individuals, instead of being solely used as a tool to derive profit. Local currencies can support businesses, create jobs, and build resilience against external influences. By using local currencies, communities can also take control of their own economic destiny, and promote their unique culture and identity. SEEDS, for example, are seeking to build a regenerative economy in which participants earn citizenship by sharing and investing 'Seeds' (their currency) into regenerative projects around the world.
Natural capital-backed assets
Natural capital-backed assets are a new and innovative way of valuing and preserving nature. They work by assigning a financial value to our natural resources and traits — i.e. trees or biodiversity. By then creating a market for these assets, companies, and organizations can actively participate in funding impact projects. The key thing here is: Nature is valued in its original, living state, rather than just as an extracted resource. Examples of natural capital-backed assets include carbon credits and biodiversity credits. Both represent a powerful tool for promoting sustainability and protecting the planet for future generations. A good example of a natural capital-backed currency is Celo's Mento stablecoin.
No-loss gambling
Gambling has been shown to exacerbate inequality. No-loss gambling is a new way to play games or participate in gambling activities, but without risking your own funds. While you won't lose money, you still have the chance to win a prize, just like with regular gambling. No-loss gambling is especially relevant for people from lower-income classes who may struggle to save money. No-loss gambling games like PoolTogether and HaloFi are actively helping people save.
Public goods funding
Public goods are available to everyone — things like parks, clean air, or free education. They benefit everyone, and everyone can access them. There are real-world public goods, like the ones we mentioned, but also digital public goods — specifically free and open source software, open datasets and open source standards. Public goods are non-excludable and non-rivalrous in nature. Non-excludable means that it is difficult or impossible to exclude people from using the good, while non-rivalrous means that the consumption of the good by one person does not diminish the availability or quality of the good for others. Gitcoin, for example, has developed a funding mechanism for public goods that weighs how many people participate in the funding along with how much money they put in.
How does Toucan implement ReFi values?
We recognize we’re in a unique situation here: Conventional VCM stakeholders value security and guardrails similar to what they are familiar with when they interact with carbon registries like Verra and Gold Standard. And more Web3-native users prefer open access and permissionless systems. We are constantly striving to achieve a healthy balance between adhering to Web3 design principles and adding the right safeguards, so everyone feels comfortable in participating, but innovation isn’t slowed down.
This can be challenging, as we’re building up a completely new system that has no precedent — but we’re optimistic that we can thread the needle. Open conversations with different parties help us understand each side's pain points, and aid us in bridging the gap between legacy actors and new market participants.
Let’s look at an example of how we’re living the ReFi ethos at Toucan.
KYC measures
We are looking into implementing reasonable KYC measures at certain points of our infrastructure while keeping other parts of the protocol open for everyone to access.

KYC at the Toucan Carbon Bridge: People interacting with Toucan's Carbon Bridge might have to undergo KYC processes in the future. The impact of this is marginal: Whoever owns carbon credits and wants to bridge them via Toucan's infrastructure will likely already have undergone KYC checks at the conventional registry, when opening an account.
No KYC to buy, deposit, or retire tokenized carbon credits: We are advocating to make sure that everyone interested in owning or trading carbon tokens can freely buy them at decentralized exchanges, integrate them into new digital products, or retire them. This is where a majority of innovation happens.
Resources
Ready for ReFi? Here are a few things that will help you dive deeper!
Our favorite articles, books, and inspiring people to follow!
Reading list — blogposts
- What is Regenerative Finance (ReFi)? Part I: The Foundations & Part II: The implementation, Letty Prados, Regen Living
- Building regenerative carbon markets with web3, Toucan Blog, Anna Watson
- What are biodiversity credits?, Toucan Blog, Kristin McDonald
- Regenerative Web 3 - The Landscape, Opportunities, and Entry Points, Adam French Gitcoin Blog
Reading list – books
- GreenPilled: How Crypto Can Regenerate The World Kevin Owocki
- Donut Economics, Kate Raworth
- Sacred Economics, Charles Eisenstein
Follow these great thinkers on socials
- Anna Lerner-Nesbitt (CEO, Climate Collective)
- Nathan Schneider (Professor & Organizer)
- Gabriela Chang (Co-Founder, Ethic Hub)
- Gregory Landua (Co-Founder, Regen Network
- Helena Merk (Founder, Spirals Protocol)
- Rene Reinsberg (Co-Founder, Celo)
- Lauren Serota (Co-Chair, WEF)
- Marc Johnson (Climate & Web3, Filecoin Green)
- Rebecca Mqamelo (Co-Founder, City3)
- Stenver Jerkku (Co-Founder, Solid World)
- Jessica Zartler (Token Engineer & governance researcher, Block Science)
- Ben West (Grants program lead, Gitcoin)
- Shuya Gong (IDEO CoLab)
- Alasdair Were (Digital Climate Markets Lead, IETA)
Toucan is building technology to unlock climate action at scale. Our digital infrastructure is helping to grow the voluntary carbon market (VCM) in a transparent and high-integrity way. It increases the flow of revenue to the most effective climate impact projects, by bringing established and nascent environmental assets on the blockchain.


